Each device connected to a network tends to have a distinct identifier. Think of it as a return address whenever you send mail. Perhaps, it’s safe to say that most networks use the TCP/IP protocol for their devices to communicate. The unique identifier in this protocol is the Internet protocol (IP) address.
What Is An IP Address?

Source: launchberg.com
IP address refers to a numerical identification label assigned to each device connected to a network. That network uses each device’s Internet protocol identification (IPID) to exchange information among themselves, without the interference of devices in other networks.
Note that two IP address standards exist, and these are:
- IPv4: An IP address that uses 32 binary bits to develop a distinct address on a specific network. IPv4 addresses tend to have four numbers that are separated by dots. One example is 192.168.1.12.
- IPv6: This is an IP address standard using 128 binary bits instead of 32. IPv6 addresses may use alphanumeric characters to form a unique identifier, such as 2001:0DB8:AC10:FE01:0000:07C0:853A:140B.
What’s The Difference Between IPv4 And IPv6?
Aside from their apparent appearances, the IPv6 standard can provide more IP addresses to online users than IPv4. It’s because IPv4 addresses only have 232 possible connections. On the other hand, IPv6 can offer about 4.3 billion unique IP addresses. Hence, using IPv6 standards may reduce the occurrences of certain issues, such as IP conflicts.
Is It Possible To Change IP Addresses?
Source: lifewire.com
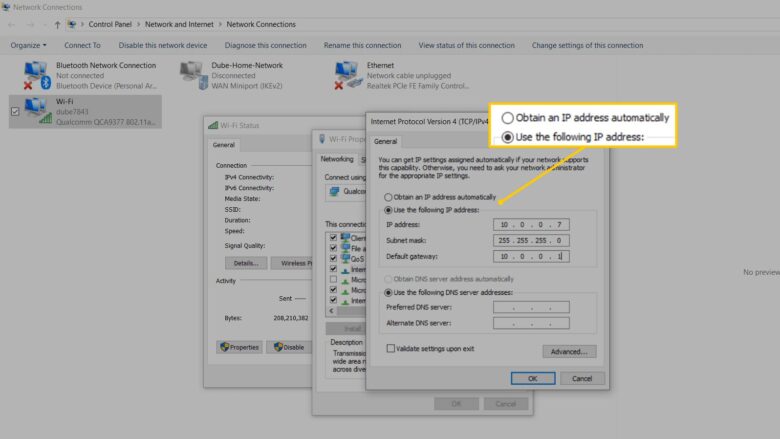
It might not be possible to change IP addresses without outside interference forcefully. For example, your computer’s IP address may change if you reset the router. However, the identifier will, still, use the same standards imposed by your Internet service provider (ISP). Therefore, the Internet will still know your location, thanks to these standards.
For example, your computer’s current IP address might be 49.194.112.12. If you change your ISP, your device may receive a new address, but it might be something like 49.194.109.9. Websites and other online portals can take advantage of that information to check your location. It’s also for this reason that you might not be able to view certain online content. Some websites tend to use geo-restricting apps and plugins to limit users to a target area.
Although it might be challenging to change your IP address, it’s quite easy to mask it with the help of a virtual private network (VPN). A VPN service encrypts your device or network’s IP address to fool servers into thinking you’re accessing the Internet from another location. If you want to know more about achieving this objective, check out reputable websites, such as securitygladiators.com.
What Is Subnet Mask?
Source: sparkmindtechnologies.com
The subnet mask is the second part of the host ID, the IP address being the first. Try to do an IP lookup on your computer. If you’re using a Windows PC, you can search for its IP address by doing the following steps:
- Right-click on the Start button.
- Choose Windows PowerShell.
- Type ipconfig/all and press Enter on your keyboard.
A set of data should come out after you hit the Enter key. But, you should now also have a clear view of various information on your PC, including IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, as well as subnet mask.
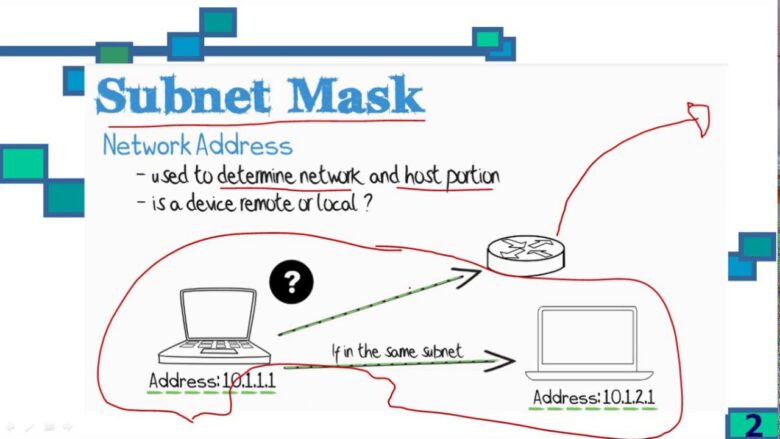
The subnet mask tends to look like 255.255.255.0. These four numbers tend to be 255 or 0. Perhaps, its vital aspect isn’t the number, but the position. It’s because the 255 or 0 signifies the division between the host ID and network. The 255 numbers will ‘mask’ the network ID, hence the name of the protocol.
Subnet masks are essential to the IP address environment. These elements help determine which IP address are local or remote to the network. Without these numbers, your device might not know how to route online traffic properly, causing network inconsistencies and errors.
Note that hackers may look into IP addresses and subnet masks for their illicit deeds, such as track emails or steal valuable online data. Therefore, stay vigilant in using public networks as these setups tend to invite unwanted guests.
How Do ISPs Assign IP Addresses?
Source: lifewire.com
Some people might think that IP addresses are plenty in a network. Although that piece of information might be true, your ISP will only assign one IP address and one subnet mask. Your router will, then, create new identifiers connected to the main address to form the network.
This process is the dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP), which is the procedure in which your ISP dynamically assigns new IP addresses to each network. Hence, your home network’s network address might change if you reset the modem. But, that particular network’s address will be unique. In other words, other networks subscribed to the ISP won’t have the same IP address.
Note that each DHCP server uses a range of IP addresses to assign. Conflicts may arise if this server runs out of addresses to offer networks. Many ISPs now use a ‘lease time’ for each IP address to help reduce these conflicts. For example, your home network’s IP address might be 49.149.102.45. But, these numbers may change after a few hours. So, if you check your IP address again after a certain period, it may alter to something like 49.149.102.57.
The process of IP address leasing is also available in many modems and routers. These devices dynamically assign and lease different identifiers to each device on the network. This process also serves the same purpose as the IP address leasing of ISPs, but on a significantly smaller scale.
Here’s a quick overview of how a DHCP server assigns addresses:
- A device ‘tells’ or sends a broadcast message to the ISP or router for the DHCP server to notice.
- The DHCP server will, then, ‘hear’ this message and send an offer for a unique address.
- The device will select the DHCP provider, acknowledging the connection.
This process may not take longer than a few seconds to complete. But, if the IP address assignment takes longer than usual, you might be experiencing some network issues. Moreover, some governments may also limit Internet use from their ISPs and their DHCP servers. These extreme cases may happen because of certain scenarios, such as political unrest.
Closing Remarks

Source: drsoft.com
Networks tend to become cluttered without the help of IP addresses and their corresponding elements. Understanding these unique identifiers may help you build and maintain networks. Furthermore, let the information posted in this article help you prevent concerns related to IP addresses, such as hacking and other cyberattacks.




