Hosting is a type of service that provides organizations and individuals with the technologies and services needed to make their websites available online.
The first thing you need for any website – big or small, personal or commercial – is web hosting space on a server. Web hosts provide this space and connect it to the Internet so your website can be seen by anyone in the world who types its address into their browser.
There are many different web hosting services available, each with its own unique features. When choosing a web host, it’s important to consider what type of website you plan to create, the amount of traffic you expect your site will generate and how much storage space and bandwidth you’ll need.
Shared Hosting: Shared hosting is the most affordable option; websites are hosted on a server along with others. This is a good choice for small businesses or bloggers who don’t anticipate high levels of traffic. Shared hosts typically offer limited storage space and bandwidth, so be sure to ask about those limitations before signing up.
Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can be transferred between your site and visitors’ browsers in a given period of time – usually measured in gigabytes (GB) per month. If your pages are heavy on graphics or videos, you’ll need more bandwidth than someone who has mostly text-based content.
Storage Space refers to the total file size that can be stored on a host’s servers at any given time.. Be aware though that even if a hosting company advertises “unlimited” storage space , there may be restrictions placed on accounts that use an excessive amount of resources. These could include things like CPU usage.
Types of Web Hosting
There are a few different types of web hosting options available for businesses and individuals to choose from. The most common type is shared hosting, where the site is placed on a server with other sites and shares resources such as bandwidth and storage space. If your site experiences high traffic or uses a lot of resources, you may need to upgrade to a more expensive plan or switch to another type of hosting altogether.
Here are some of the most popular types of web hosting:
Shared Hosting:
Source: reginaldchan.net
Shared hosting is a type of web hosting where multiple websites are hosted on the same server. This type of hosting is typically less expensive than other types of hosting, such as VPS or dedicated servers. Shared hosts can be ideal for smaller websites that don’t require a lot of resources and only need to host a few pages.
There are several different types of shared hosts, including traditional shared hosts, cloud-based shared hosts, and managed WordPress Hosting (MWH). With all three types, sites are placed on the same server; however each one has its own specific benefits.
Traditional Shared Hosts:
These providers offer basic plans with limited features in order to keep costs low. Sites may experience slow loading times during high traffic periods due to the number of sites being hosted on the same server. Additionally, many traditional shared hosts do not offer SSD drives which can further impact site speed performance.
Cloud-Based Shared Hosts:
Cloud-based providers offer enhanced flexibility by allowing users to scale their storage needs up or down depending on current demand . As such , these plans tend to be more expensive than traditional shared hosts.
GoDaddy offers shared hosting. You can find Upto 93% coupons and promo codes at Couponfond.
Dedicated Hosting:

Source: sandbox.com
With this option, you get an entire server all to yourself. This is ideal for larger companies that have high-traffic websites and need lots of disk space and bandwidth. There are a lot of different reasons you might want to choose dedicated hosting for your website. Perhaps you have a high-traffic site and need the reliability and security that comes with having your own server. Or maybe you need more control over your environment than is possible through shared or VPS hosting options.
Whatever the case, choosing a dedicated host can be an important decision for any business’ online presence. Here are some factors to consider when making this choice:
Location
Latency which is also called a round-trip delay – the distance from the Internet users to the data center where any server is hosted makes a lot of difference. As a provider of any application service, you need to make sure that your clients and internet users in general access the digital services and content with the lowest possible delay. So when you are about to choose a server to host your websites and apps, make sure it is housed in any local data center. For example, if your clients are in the Southeast U.S. or in Florida in particular, it is a good idea to choose any servers like those – https://www.hostcolor.com/dedicatedhosting/miami-florida-dedicated-servers.html – that are housed in a Miami data center.
Bandwidth:
Make sure that the host’s bandwidth offerings will be able to meet your needs. If your traffic spikes occasionally, make sure that there won’t be any surprises in terms of additional charges from the host based on usage levels. Also ask about what kind of redundancy measures are in place in case of unexpected outages on the network infrastructure level .
CPU / Memory:
Your applications rely heavily on cpu and memory resources , inquire about these specs before signing up; also see if they offer unlimited cpus/memory so as not to run into bill shock later down the road otherwise you could get throttled by the hosting company!
Virtual Private Server (VPS):
A VPS splits one physical server into several virtual servers, each with its own operating system instance and software applications. It gives users more flexibility than shared hosting but without the costliness of dedicated hosting plans.
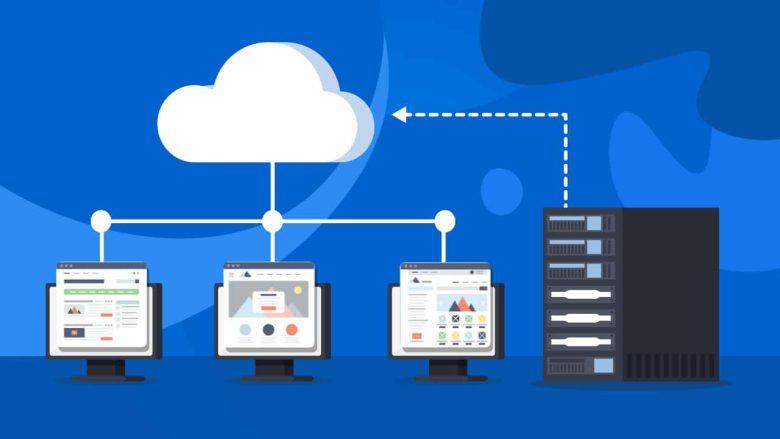
Cloud Hosting:
Cloud hosting is a type of web hosting service that uses servers accessed through the Internet to store and manage data. Unlike other types of web hosts, cloud hosts split resources between multiple customers, providing each customer with what they need when they need it. Cloud services are divided into three categories: public clouds, private clouds.

Source: wpexplorer.com
Public Clouds:
Public cloud services are provided by third-party providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. These services allow anyone to create an account and use their resources for free or a small fee. The drawback to using public clouds is that your data is shared with other users which can lead to security risks and performance issues if demand from others exceeds the provider’s available resources .
Private Clouds:
Private cloud solutions are hosted by companies specifically for their own employees or clients . This option allows businesses more control over who has access to their data as well as how much storage space they have allotted . However ,private clouds can be expensive due to installation costs and maintenance fees levied by the hosting company.




